Hyderabad, India
June 23, 2021

A research team led by Prof. Appa Rao Podile, faculty in the Department of Plant Sciences, UoH, in a three-year collaboration with two groups in the United Kingdom (Prof. Philip Poole’s group at the Department of Plant Sciences, University of Oxford, and Dr. Andrew Neal at Rothamsted Research) has made a major breakthrough in plant symbiosis studies.
Plant symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria (rhizobia) is a key to sustainable agriculture. Pulses and other legumes develop complex symbiotic associations with rhizobia at root nodules—rhizobia ‘fix’ and supply nitrogen to the host plants; plants, in return, provide carbon and energy.

Pigeon pea plant
Pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan), a climate-smart pulse crop of Indian origin, is widely grown in the tropical drylands around the globe. Popularly known as ‘Arhar’, ‘Toor’ or ‘Tuvar’ in the Indian household, pigeon pea serves as a primary protein source for millions of poor people in developing countries. However, the crop often suffers from inconsistent yields and poor nodule formation in India. Bradyrhizobium is the most common pigeon pea symbiont in Indian soils. Understanding the interactions of ‘Arhar’ with different rhizobia could help in finding a solution for the poor nodulation that can bring consistency in its yield. While there have been multiple attempts to select the best N2-fixing symbionts, there are no reliable strains available for geographically widespread use.
The team headed by Prof Podile and including three Ph.D. scholars, Ch. Danteswari, Anirban Basu, and PVSRN Sarma, assessed the microbial community associated with pigeon pea roots in different soil types with a comprehensive approach and found the root microbial composition was primarily determined by the plant developmental stage and soil type rather than the plant variety. The study concluded that the low nodulation efficiency of pigeon pea is due to the inadequate presence of appropriate symbionts in the soils. Indian soils were mainly found to harbor non-symbiotic Rhizobium spp., rather than symbiotic (nodule-forming) Bradyrhizobium spp.
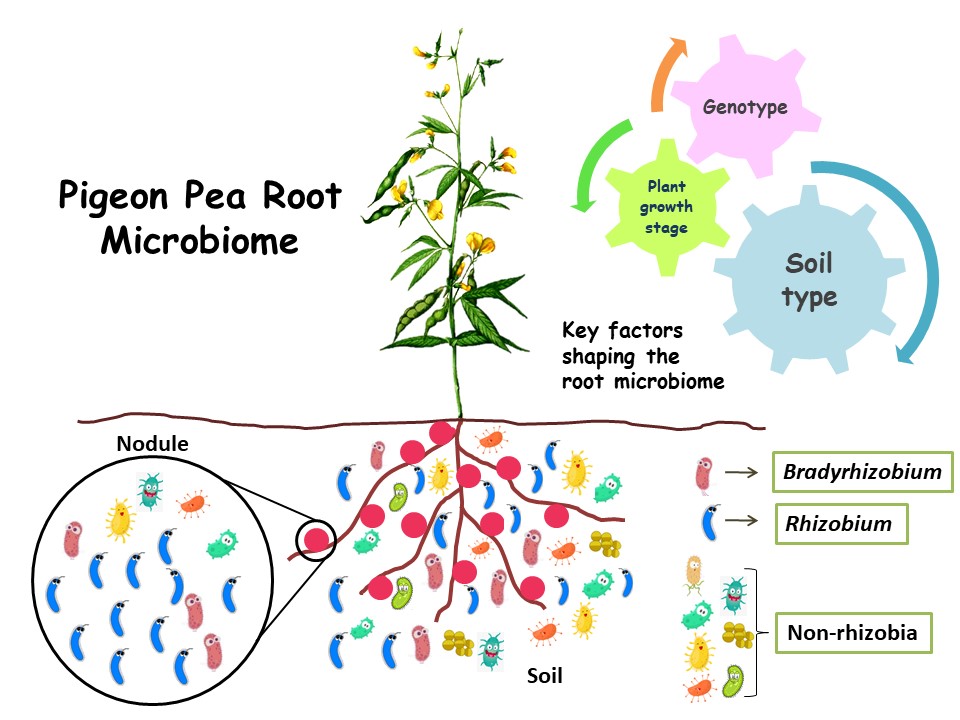
Cartoon depicting the pigeon pea root and nodule microbiome, which consists of different rhizobia (including Bradyrhizobium and Rhizobium) and non-rhizobia species. The plant developmental stage and soil type primarily shape the root microbial composition, while the plant variety (genotype) plays a minor role. Rhizobium in the soil out competes Bradyrhizobium for pigeon pea root (nodule) colonization.
These findings will pave the way for selecting and applying appropriate symbionts to improve pigeon pea yields and nodulation under Indian conditions. It suggests that the inoculant strain selection of symbionts for pigeon pea should be based not only on their nitrogen fixation potential but, more importantly, on their competitiveness in agricultural soils.
The project was supported by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India, and Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), UK. The results will be published in a high-impact journal entitled ‘mBio’ of the American Society for Microbiology (ASM) in association with the American Academy of Microbiology, USA.