South Perth, Western Australia
March 17, 2005
|
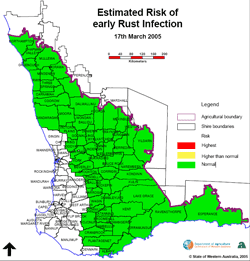 |
|
Click
on map to enlarge (PDF file) |
Dry summer
conditions have greatly reduced opportunities for wheat rust
diseases, which are expected to have a much lower impact this
year compared to 2004.
Each year around St Patrick’s day,
the Department of
Agriculture, Western Australia provides a regional
assessment of potential rust risk based on the prevalence of
summer rain and subsequent green cereal re-growth.
Department plant pathologist Geoff Thomas said
stem, stripe and leaf rust needed living host plants to survive
and the greatest yield impacts occurred when early infections
developed from over summer build up – the so called
‘green-bridge’ high risk scenario.
“Rainfall in the period December to February has
been average to well below average throughout all areas of the
Western Australian wheatbelt,” Mr Thomas said.
“With few opportunities for wheat re-growth,
green bridge sites are largely absent.
“This lack of green-bridge reduces the ability of
all rusts to survive through the harsh summer conditions.”
The lack of significant summer rain has reduced
overall risk significantly throughout the wheatbelt and as a
result, rust risk for 2005 is expected to be less than that
observed in 2003 and 2004.
While the potential for rust outbreaks exist
every season, a dry summer normally results in fewer and later
rusts outbreaks and without significant occurrence of summer
re-growth in 2004/05, the build up of rust will be slowed.
Mr Thomas said the Department would provide a
further rust risk assessment if unusual regional rainfall
occurred and the risk changed.
“While growers in many areas are reliant on good
early rains, ongoing dry conditions may reduce the requirement
for costly management of wheat re-growth prior to the onset of
mainstream cropping,” he said. |